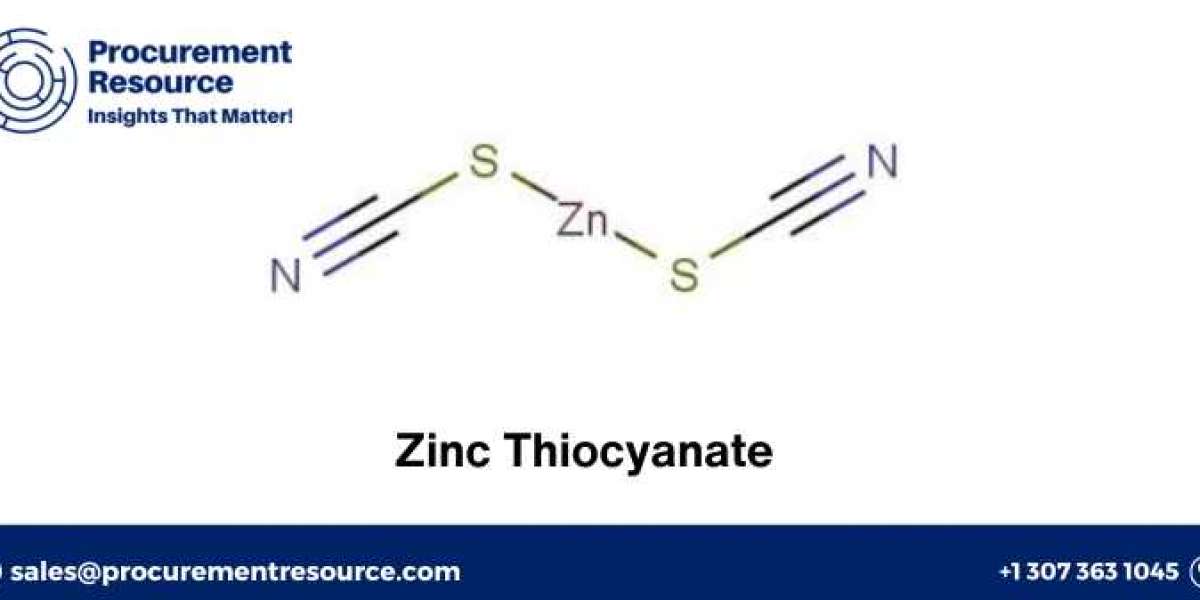
Zinc thiocyanate (Zn(SCN)2) is an important inorganic compound widely used in various industrial applications, including chemical synthesis, electroplating, and as a catalyst. Understanding the production process, associated costs, and raw materials involved in manufacturing zinc thiocyanate is crucial for businesses and researchers in the chemical industry. This blog provides a comprehensive overview of the zinc thiocyanate production process, production cost report, manufacturing report, and raw material costs.
Zinc Thiocyanate Production Process
The production of zinc thiocyanate primarily involves the reaction between zinc salts and thiocyanate salts in an aqueous medium. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
Preparation of Solutions:
- Zinc Salt Solution: Typically, zinc chloride (ZnCl2) or zinc sulfate (ZnSO4) is dissolved in water to form a zinc salt solution.
- Thiocyanate Salt Solution: Sodium thiocyanate (NaSCN) or potassium thiocyanate (KSCN) is dissolved in water to form a thiocyanate solution.
Reaction: The zinc sulfate solution is slowly added to the potassium thiocyanate solution under constant stirring. The reaction takes place at room temperature, resulting in the formation of zinc thiocyanate and potassium sulfate as by-products.
Request For Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/zinc-thiocyanate/request-sample
Filtration and Washing:
- The precipitated zinc thiocyanate is separated from the reaction mixture using filtration.
- The solid product is washed with distilled water to remove any unreacted salts and impurities.
Drying:
- The washed zinc thiocyanate is dried at a controlled temperature to obtain the final product in its pure form.
Quality Control:
- The dried product undergoes quality control tests to ensure it meets the required purity and specifications.
Production Cost Report
The production cost of zinc thiocyanate can be divided into several components:
Raw Material Costs:
- Zinc chloride or zinc sulfate
- Sodium thiocyanate or potassium thiocyanate
- Distilled water
Utility Costs:
- Electricity for stirring and drying
- Water for washing and preparation of solutions
Labor Costs:
- Wages for workers involved in the production process
Equipment and Maintenance Costs:
- Cost of reactors, filters, dryers, and other equipment
- Regular maintenance and repairs
Quality Control Costs:
- Analytical instruments and reagents
- Labor costs for quality testing
Overhead Costs:
- Administrative expenses
- Factory overheads such as rent, insurance, and utilities
Manufacturing Report
A detailed manufacturing report for zinc thiocyanate includes the following sections:
Process Description:
- A detailed step-by-step description of the production process, including the chemical reactions involved.
Equipment and Machinery:
- List of equipment used in the production process along with their specifications and operational details.
Production Capacity:
- The maximum and average production capacity of the manufacturing unit.
Quality Control Procedures:
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs) for quality control tests to ensure product purity and compliance with industry standards.
Safety and Environmental Measures:
- Safety protocols for handling chemicals and operating machinery.
- Measures to minimize environmental impact, including waste management and emissions control.
Cost Analysis:
- Detailed breakdown of production costs, including raw materials, utilities, labor, equipment, and overheads.
Raw Material Cost
The cost of raw materials is a significant factor in the overall production cost of zinc thiocyanate. Here’s an overview of the key raw materials and their typical costs:
Zinc Chloride (ZnCl2) / Zinc Sulfate (ZnSO4):
- Zinc salts are the primary source of zinc ions in the production process.
- The cost of zinc chloride and zinc sulfate can vary based on purity, supplier, and market conditions.
Sodium Thiocyanate (NaSCN) / Potassium Thiocyanate (KSCN):
- Thiocyanate salts provide the thiocyanate ions necessary for the formation of zinc thiocyanate.
- Similar to zinc salts, the cost of sodium thiocyanate and potassium thiocyanate depends on factors like purity and supplier.
Distilled Water:
- Used for dissolving raw materials and washing the final product.
- The cost is relatively low but essential for maintaining product purity.
Conclusion
The production of zinc thiocyanate involves a straightforward chemical reaction between zinc salts and thiocyanate salts. The production cost is influenced by raw material prices, utility costs, labor, equipment, and overhead expenses. Understanding these factors is crucial for efficient manufacturing and cost management. By optimizing the production process and sourcing raw materials at competitive prices, manufacturers can produce high-quality zinc thiocyanate while maintaining profitability.